Advantages of Thermal Imaging Night Vision
The need for reliable security solutions has never been more critical, with threats evolving in complexity and sophistication. Thermal imaging night vision has emerged as a game-changer, offering capabilities that surpass those of traditional surveillance systems. By capturing heat signatures rather than relying on visible light, these systems ensure uninterrupted monitoring regardless of lighting conditions, creating a robust line of defence against potential threats.
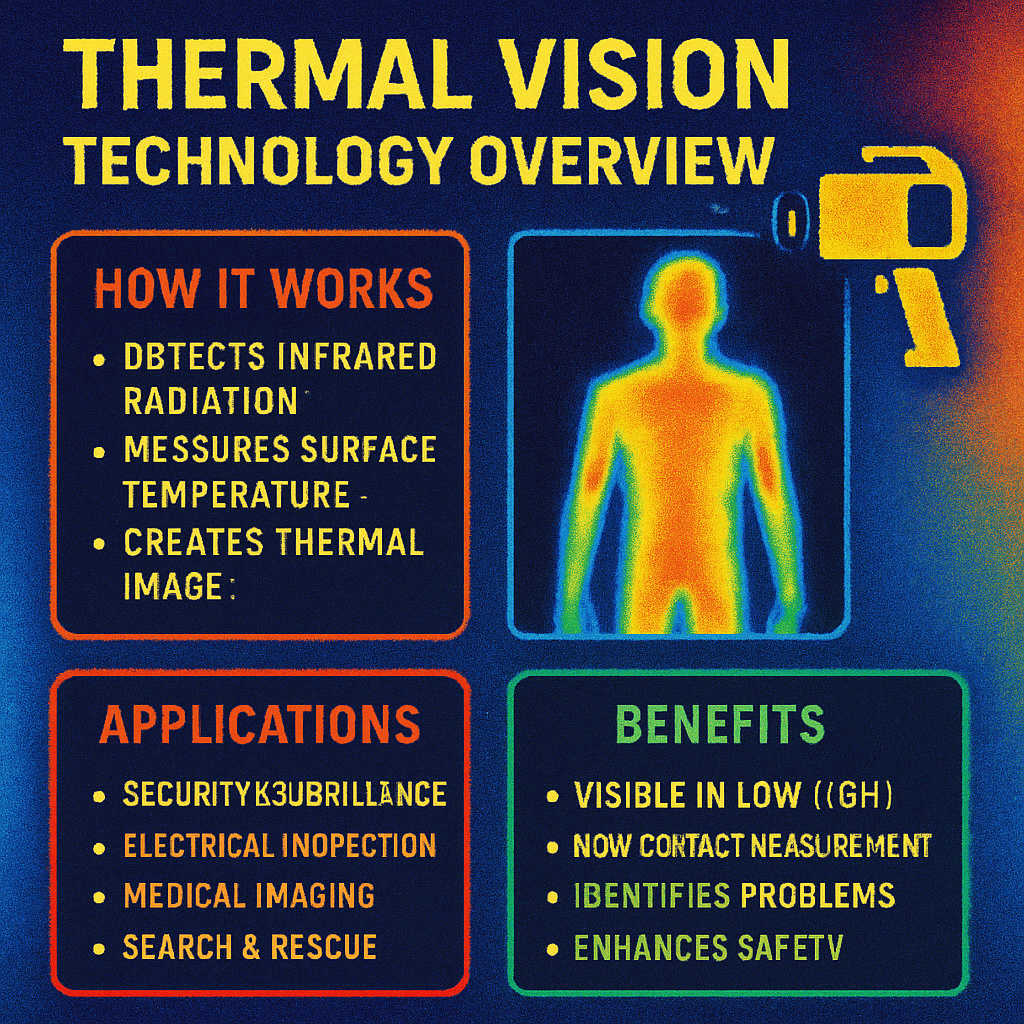
How Does Thermal Imaging Work?
Thermal imaging night vision devices utilise infrared technology to detect heat emitted by objects, translating it into an image. Unlike conventional cameras that rely on visible light, thermal cameras capture the infrared radiation, which is a thermal signature, emitted by all objects above absolute zero temperature. This capability enables them to create a visual representation based solely on temperature differences, thereby allowing visibility in total darkness, fog, or smoke.
This technology works by detecting the minute differences in temperature between various objects and their surroundings. It provides a crucial advantage in scenarios where traditional cameras might fail, such as during night-time or in environments obscured by elements like fog or smoke. With the ability to perceive heat, these cameras can capture images irrespective of the lighting conditions, offering a reliable surveillance solution around the clock.
The Science Behind Night Vision Thermal Cameras
Night vision thermal imaging1 cameras operate on the principle of detecting temperature variations. Each pixel in a thermal image corresponds to a specific temperature, allowing the camera to render a detailed picture based on heat differentials. This attribute makes thermal cameras indispensable in scenarios where traditional night vision devices might falter due to low-light conditions.
The intricate science of thermal imaging involves converting infrared radiation into electrical signals, which are then processed to form an image. These cameras are equipped with a special sensor called a microbolometer, which measures heat emitted by objects. This sensor captures the thermal energy and translates it into a visible image, enabling users to discern between objects based on their thermal signatures. This capability is particularly valuable in environments where other forms of surveillance might be compromised.
Key Advantages of Thermal Imaging Night Vision

Enhanced Visibility in Absolute Darkness
One of the most significant advantages of thermal imaging night vision is its ability to provide visibility in complete darkness. Traditional night vision devices amplify existing light, which can be rendered ineffective in pitch-black environments. Conversely, thermal cameras do not require any ambient light, making them ideal for nocturnal surveillance.
These cameras offer a unique advantage by functioning independently of external light sources, allowing for consistent monitoring throughout the night. This feature is especially beneficial for large outdoor areas where lighting might be sporadic or nonexistent. By offering a comprehensive view in the dark, thermal cameras ensure that security personnel can maintain situational awareness, detecting threats before they escalate into serious incidents.
Improved Detection of Camouflaged Threats
Thermal vision technology excels at detecting objects that might be concealed by camouflage or hidden in natural environments. This capability is particularly advantageous in security operations where identifying human intruders or animals, even when concealed, is critical. By recognizing the heat signature, thermal cameras can uncover threats that would otherwise remain undetected with standard visual surveillance methods.
This advantage is crucial in environments where individuals or objects might blend into their surroundings, such as heavily wooded areas or urban settings with complex infrastructures. Thermal cameras can cut through visual noise, identifying heat sources that are otherwise invisible to the naked eye. This makes them indispensable tools for perimeter security, search and rescue missions, and wildlife monitoring, where stealth and camouflage are often employed.
Weather Resilience and Environmental Adaptability
Unlike optical systems, thermal imaging night vision devices maintain their effectiveness in adverse weather conditions such as fog, rain, or snow. This adaptability ensures continuous surveillance without the interference typically encountered with visual cameras, which can have their view obstructed by environmental factors.
In challenging weather conditions where visibility is severely compromised, thermal imaging stands out as a reliable solution. Whether it’s heavy rain, dense fog, or a snowstorm, thermal cameras can penetrate these barriers, ensuring that surveillance operations continue unabated. This resilience makes them a preferred choice for outdoor security, where weather variability is a constant challenge, ensuring that critical areas remain under watch regardless of environmental conditions.
Integration with Advanced Security Systems
Seamless Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Thermal imaging night vision cameras can be integrated into existing security systems with relative ease. Many modern security networks are designed to accommodate thermal cameras, allowing for a straightforward upgrade path. This integration enhances overall security capabilities without necessitating a complete overhaul of the current infrastructure.
By leveraging existing infrastructure, organisations can enhance their security posture cost-effectively, ensuring that their investment in thermal technology yields maximum returns. The ability to integrate with current systems also means that organisations can scale their security operations as needed, adding thermal capabilities where they are most needed without disrupting ongoing operations.
Complementary Role with Artificial Intelligence
Incorporating artificial intelligence with thermal vision technology2 further enhances its utility. AI-driven analytics can process thermal images to detect unusual patterns or movements, offering real-time alerts and insights. For security managers, this means a proactive approach to threat detection, enabling quicker responses to potential security breaches.
With AI, thermal imaging systems can be programmed to recognise specific threats, learning and adapting over time to improve accuracy. This synergy allows for advanced functionalities such as automatic threat recognition, behaviour analysis, and predictive alerts, transforming security operations from reactive to proactive. The combination of AI and thermal imaging represents a significant leap forward in surveillance capabilities, allowing security teams to focus on strategic decision-making rather than constant monitoring.
Applications Across Various Security Domains

Military and Defence Operations
Thermal imaging has long been a staple in military applications, where its ability to detect threats in challenging environments is invaluable. Night vision thermal cameras are used for reconnaissance, border security, and tactical operations, providing armed forces with a strategic advantage.
In military operations, the ability to detect heat signatures from a distance can be a decisive factor in mission success. Thermal cameras assist in identifying enemy positions, tracking troop movements, and guiding operations in low-visibility conditions. Their use extends beyond the battlefield, aiding in peacekeeping missions and humanitarian efforts by ensuring safety and situational awareness in volatile regions.
Commercial and Industrial Security
In commercial and industrial settings, thermal imaging cameras are employed to monitor perimeters, detect unauthorised access, and prevent theft. Their ability to function autonomously in low-light conditions makes them particularly useful for night-time security operations in warehouses, factories, and construction sites.
For businesses, thermal cameras provide a robust solution to safeguard assets and infrastructure. They can monitor large areas with minimal supervision, reducing the need for extensive security personnel. This efficiency not only enhances security but also offers cost savings, as thermal imaging reduces the reliance on multiple conventional cameras, lowering both equipment and operational costs.
Wildlife Monitoring and Conservation
Beyond conventional security uses, thermal imaging night vision plays a crucial role in wildlife monitoring and conservation efforts. By tracking animal movements and behaviours without disturbing their natural habitats, conservationists can gather important data to support ecological studies and preservation initiatives.
Thermal cameras offer a non-invasive method to study wildlife, providing insights into animal behaviour, population dynamics, and habitat usage. This information is vital for developing effective conservation strategies, protecting endangered species, and managing human-wildlife conflict. The use of thermal imaging in conservation also helps minimise human impact on fragile ecosystems, ensuring sustainable wildlife management.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementation
Addressing Cost and Accessibility
While the benefits of thermal imaging night vision are substantial, the cost can be a barrier to adoption. However, as technology advances and manufacturing costs decrease, these devices are becoming more accessible to a broader range of security operations. Investing in thermal imaging technology can result in long-term cost savings by reducing the need for multiple surveillance devices and minimising false alarms.
As the market for thermal imaging expands, economies of scale are helping to lower prices, making these systems a viable option for small to medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, the reduction in false alarms due to the precise detection capabilities of thermal cameras leads to operational efficiencies and cost savings over time. Organisations that invest in thermal technology can expect a return on investment through enhanced security and reduced operational costs.
Ensuring User Training and Understanding
For effective implementation, it is essential that security personnel receive adequate training on the operation and interpretation of thermal images. Understanding the nuances of thermal data and integrating it with existing security protocols can significantly enhance the efficacy of surveillance operations.
Proper training ensures that personnel can accurately interpret thermal imagery, distinguishing between actual threats and benign heat sources. This knowledge is crucial for making informed decisions and preventing unnecessary responses to false alarms. By investing in comprehensive training programs, organisations can maximise the benefits of thermal imaging technology, ensuring that it enhances rather than complicates security operations.
Conclusion: The Future of Security Operations
Thermal imaging night vision represents a pivotal advancement in security technology, offering unparalleled advantages in visibility, detection, and adaptability. For security managers tasked with safeguarding assets and personnel, integrating this technology into existing systems can transform operational efficacy and responsiveness.
By embracing thermal vision technology, security operations can shift from a reactive to a proactive posture, anticipating threats before they manifest. As the technology continues to evolve, its role in revolutionising security frameworks will only become more pronounced, cementing its status as an indispensable tool in the arsenal of modern security solutions.
In the face of emerging threats and the ever-growing demand for enhanced security measures, thermal imaging stands out as a critical component of future-ready security systems. Its ability to provide consistent, reliable surveillance under any conditions ensures that organisations can remain vigilant and responsive, safeguarding their assets and personnel with confidence. As we advance, the integration of thermal imaging with other cutting-edge technologies promises to push the boundaries of what is possible in security, paving the way for safer and more secure environments across all sectors.
